2nd OCTOBER 1934 INDIAL NAVAL FORCE ESTABLISHED - ROYAL INDIAN NAVY
Indian Armed Forces
The Government of India is responsible for ensuring the defence of India and every part thereof. The Supreme Command of the Indian Armed Forces vests in the President. The responsibility for national defence rests with the Cabinet. This is discharged through the Ministry of Defence, which provides the policy framework and wherewithal to the Armed Forces to discharge their responsibilities in the context of the defence of the country. The Indian Armed Forces comprise of three divisions – Indian Army, Indian Navy, and the Indian Air Force.
Check more important links.
Check more important links.
Indian Army
The Indian subcontinent had witnessed the cohesive concentration of many Empires in the quest for control of military power, and governance of the State. As time rolled by, societal norms found an ethos in the workplace, the system of rights and privileges, and service under the flag.
The Indian Army, as we know it today became operational after the Country gained independence from British colonialism. The Indian Army's HQ is located in New Delhi and functions under the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is responsible for the command, control, and administration as a whole. The Army is divided into six operational commands (field armies) and one training command, each under the command of a Lieutenant General, who has an equal status to the Vice-Chief of Army Staff (VCOAS), working under the control of Army HQ in New Delhi.
More about the Indian Army.
More about the Indian Army.
Indian Navy
The foundation of the modern Indian Navy was laid in the seventeenth century when the East India Company had established a maritime force, thereby graduating in time to the establishment of the Royal Indian Navy in 1934. The Headquarters of the Indian Navy is located in New Delhi, and is under the command of the Chief of the naval staff – an Admiral. The Indian navy is deployed under three area commands, each headed by a flag officer. The Western Naval Command is headquartered in Bombay on the Arabian Sea; the Southern Naval Command in Kochi (Cochin), in Kerala, also on the Arabian Sea; and the Eastern Naval Command in Vishakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, on the Bay of Bengal.
More about the Indian Navy.
More about the Indian Navy.
Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force was officially established on 8th October 1932, and on 1st April 1954, Air Marshal Subroto Mukherjee, one of the founding members of the Air Force took over as the first Indian Chief of Air Staff. With the passage of time, the Indian Air Force undertook massive upgrading of its aircraft and equipments, and as part of the process, it introduced more than twenty new types of aircrafts. The last decade of the twentieth century saw a phenomenal change in the structure of the Indian Air Force with induction of women into the Air Force for short service commissions. It was also a time when the Air Force undertook some of the most perilous operations ever undertaken.
More about the Indian Air Force.
More about the Indian Air Force.
Source: National Portal Content Management Team 
Royal Indian Navy
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Royal Indian Navy | |
|---|---|
| Active | 1612 – 26 January 1950 |
| Country | |
| Branch | Navy |
| Garrison/HQ | Bombay |
| Engagements | Seven Years' War Capture of East India Company ship Nautilus Anglo-Burmese Wars First Opium War Second Opium War First World War Second World War |
| Insignia | |
| Naval Ensign (1928-1950) | 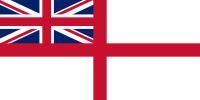 |
| Naval Ensign (1879-1928) & Naval Jack (1928-1947) |  |
The Royal Indian Navy (RIN) was the naval force of British India and the Dominion of India. Along with the Presidency armies, later the Indian Army, and from 1932 the Indian Air Force, it was one of the Armed Forces of British India.
From its origins in 1612 as the East India Company's Marine, the Navy underwent various changes, including changes to its name. Over time it was named the Bombay Marine, Her Majesty's Indian Navy, Her Majesty's Indian Marine and the Royal Indian Marine, until being renamed the Royal Indian Navy in 1934. However, it remained a relatively small force until the Second World War, when it was greatly expanded.
After the partition of India into two independent states in 1947, the Navy's assets and personnel were split with the new Royal Pakistan Navy. Approximately two thirds of the fleet remained with the Union of India, as did all land assets within its territory, and this force, still under the name of "Royal Indian Navy", became the navy of the Dominion of India until the country became a republic on 26 January 1950. It was then renamed as the Indian Navy.
Contents
[hide]History[edit]
Main article: History of the Indian Navy
East India Company[edit]
1612–1686[edit]
Further information: East India Company and Company rule in India
The East India Company was established in 1599, and it began to create a fleet of fighting ships in 1612, soon after Captain Thomas Best defeated the Portuguese at the Battle of Swally. This led the Company to build a port and to establish a small navy based at Suvali, near Surat, Gujarat, to protect its trade routes. The Company named the force the 'Honourable East India Company's Marine', and the first fighting ships arrived on 5 September 1612.[1]
This force protected merchant shipping off the Gulf of Cambay and the rivers Tapti and Narmada. The ships also helped map the coastlines of India, Persia and Arabia.[2]
1686–1830[edit]
In 1686, with most of English commerce moving to Bombay, the force was renamed the 'Bombay Marine'.[1] This force fought the Marathas and the Sidis and took part in the Anglo-Burmese Wars. While it recruited Indian sailors extensively, it had no Indian commissioned officers.[2]
Commodore William James was appointed to command the Marine in 1751. On 2 April 1755, commanding the Bombay Marine Ship Protector, he attacked the Maratha fortress of Tulaji Angre at Severndroog between Bombay and Goa. James had instructions only to blockade the stronghold, but he was able to get close enough to bombade and destroy it.[2]
In February 1756, the Marine supported the capture of Gheriah (now Vijaydurg) by Robert Clive and Admiral Watson and was active in skirmishes against the French, helping to consolidate the British position in India.[2]
1830–1858[edit]
In 1830, the Bombay Marine was renamed the "Indian Navy". The British capture of Aden increased its commitments, leading to the creation of the "Indus Flotilla". The Navy then took part in the First Opium War of 1840.[2]
In 1852, at the outset of the Second Anglo-Burmese War, ships of Her Majesty's Indian Navy joined a Royal Navy force under the command of Admiral Charles Austen to assist General Godwin in the capture of Martabanand Rangoon.[3]
Direct British rule in India[edit]
After the end of Company rule in India following the Indian rebellion of 1857, the force came under the command of the British government of India and was formally named "Her Majesty's Indian Navy".[2]
1858–1934[edit]
Her Majesty's Indian Navy resumed the name "Bombay Marine" from 1863 to 1877, when it was renamed "Her Majesty's Indian Marine" (HMIM). The Marine then had two divisions; an Eastern Division at Calcutta and a Western Division at Bombay.
In recognition of its fighting services, HMIM was given the title of "Royal Indian Marine" in 1892. By this time it consisted of over fifty vessels.[4][dead link] In 1905, the service was described as having "Government vessels engaged in troop-ship, surveying, police or revenue duties in the East Indies".[5]
When mines were detected off the coasts of Bombay and Aden, during the First World War, the Royal Indian Marine went into action with a fleet of minesweepers, patrol vessels and troop carriers. Besides patrolling, the Marine ferried troops and carried war stores from India to Mesopotamia (now Iraq), Egypt and East Africa.
The first Indian to be granted a commission was Engineer Sub-Lieutenant D. N. Mukherji, who joined the Royal Indian Marine as an officer on 6 January 1923.[6]
1934–1945[edit]
In 1934 the Royal Indian Marine changed its name, with the enactment of the Indian Navy (Discipline) Act of 1934. The Royal Indian Navy was formally inaugurated on 2 October 1934, at Bombay.[7] Its ships carried the prefixHMIS, for His Majesty's Indian Ship.[8]
At the start of the Second World War, the Royal Indian Navy was small, with only eight warships. The onset of the war led to an expansion in vessels and personnel described by one writer as "phenomenal". During the War, the Women's Royal Indian Naval Service was established, for the first time giving women a role in the navy, although they did not serve on board its ships.[7]
The sloops HMIS Sutlej and HMIS Jumna played a role in Operation Husky, the Allied invasion of Sicily.[9][dead link]
Mutiny of 1946[edit]
Main article: Royal Indian Navy Mutiny
In February 1946, Indian sailors launched the Royal Indian Navy Mutiny on board more than fifty ships and in shore establishments, protesting about alleged discrimination against Indian sailors and officers by the British during the war.[10] The mutiny found widespread support and spread all over India, including the Army and the Air Force. A total of seventy-eight ships, twenty shore establishments and 20,000 sailors were involved in this mutiny.
Independence and Partition of India, 1947[edit]
Main article: Partition of India
Following India's independence in 1947 and the ensuing partition, the Royal Indian Navy was divided between the newly independent Union of India and Dominion of Pakistan, and the Armed Forces Reconstitution Committee divided the ships and men of the Royal Indian Navy between India and Pakistan. The division of the ships was on the basis of two-thirds of the fleet to India, one third to Pakistan.[11]
The committee allocated to the n Pakistan Navy" (RPN) three of the seven active sloops, HMIS Godaveri, HMIS Hindustan and HMIS Narbada, four of the ten serviceable minesweepers, two frigates, two naval trawlers, four harbour launches and a number ofharbour defence motor launches. 358 personnel, and 180 officers, most of whom were Muslims or Europeans, volunteered to transfer to the RPN. India retained the remainder of the RIN's assets and personnel, and many British officers opted to continue serving in the RIN.[7]
On 26 January 1950, when India adopted its current constitution and became a republic, the "Royal Indian Navy" was renamed the Indian Navy. The Union Jack in the canton of the White Ensign was replaced with the Tiranga. Its vessels were redesignated as "Indian Naval Ships", and the "HMIS" ship prefix for existing vessels was changed to 'INS'.[12]
Commanding Officers[edit]
Partition of ships, 1947[edit]
| Vessel type | India | Pakistan |
|---|---|---|
| Frigate |
|
|
| Sloop | ||
| Corvettes | ||
| Minesweeper | ||
| Survey vessel |
| |
| Trawler |
|
|
| Motor minesweeper(MMS) |
|
|
| Motor launch (ML) |
| - |
| Harbour Defence Motor Launch (HDML) |
|
|
| Tanker | ||
| Miscellaneous | All existing landing craft |
See also[edit]
Search Results
The Royal Indian Navy - Second World War - YouTube
www.youtube.com/watch?v=NZAUjc1ho2o
Dec 15, 2008 - Uploaded by jaganpvs
Rare footage of the Royal Indian Navy seamen from World War Two. This is part of the news reels released by ...1946 - Royal Indian Navy mutiny...Havent heard about it ...
www.youtube.com/watch?v=RUYFYpP5R-w
Mar 28, 2013 - Uploaded by Subhash1897
India Got Freedom because of this Royal Indian NavyMutiny(1946). Just look at the timeline of indian history ...Royal Indian Navy Sailors Sinking A Japanese Submarine ...
www.youtube.com/watch?v=H1pu3YePg3M
Jul 23, 2011 - Uploaded by Luptonga
A video clip showing Indian sailors serving in the then Royal Indian Navy during the World War 2. They are ...Royal Indian Navy flag flying on ship Royal Indian Navy ...
www.gettyimages.com/.../royal-indian-navy...royal-in...
Indian Navy marching contingent on Republic Day - YouTube
www.youtube.com/watch?v=6I8JLYr5kZ0
Sep 30, 2013 - Uploaded by WildFilmsIndia
The Indian Navy can trace its lineage back to the Royal Indian Navy, however the modern navy as it is known ...Classes at Royal Indian Navy training station sailors ...
www.gettyimages.com/...royal-indian-navy.../5098399...
Indian Navy Rescue Aircrew - British Pathé
www.britishpathe.com/.../indian-navy-rescue-aircrew
Royal indian navy targetting the pakistan navy just beware ...
www.youtube.com/watch?v=GIA0vjFtW2k
Oct 3, 2011 - Uploaded by kumkum8057
Indian Navy sinks pirate ship Video, Video clips, Featured videos.India - YouTube
www.youtube.com/watch?v=EL24fpxrrpI
Mar 29, 2015 - Uploaded by Him Fact
Meet Past , Current and future Aircraft Carrier of Indian Navy INS . ... in 1943 under the name Hercules for the ...WS Sailors standing outside for inspection at the Royal ...
www.gettyimages.com/detail/...royal.../509839941
Stay up to date on results for Royal Indian Navy.
Create alertSearch Results
Royal Indian Navy - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Royal_Indian_Navy
The Royal Indian Navy (RIN) was the naval force of British India and the Dominion of India. Along with the Presidency armies, later the Indian Army, and from ...Royal Indian Navy mutiny - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Royal_Indian_Navy_mutiny
The Royal Indian Navy revolt (also called the Royal Indian Navy mutiny or Bombay mutiny) encompasses a total strike and subsequent revolt by Indian sailors of ...History of the Indian Navy - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_the_Indian_Navy
Jump to The Royal Indian Navy in World War II - [edit]. In 1934, the Royal Indian Marine became the Royal Indian Navy (RIN). Ships of the RIN received ...Genesis of Indian Navy : About Indian Navy : Indian Navy
www.indiannavy.nic.in/about-indian-navy/genesis-indian-navy
In 1830, the Bombay Marine was renamed Her Majesty's Indian Navy. ... On India attaining Independence, the Royal Indian Navy consisted of 32 ageing vessels ...Royal Indian Navy (RIN) Mutiny 1946 - General Knowledge ...
www.gktoday.in/royal-indian-navy-rin-mutiny-1946/
Oct 30, 2011 - On February 18, 1946, a section of non-commissioned officers and sailors known as Ratings, serving in the Royal Indian Navy, mutinied ...HyperWar: The Royal Indian Navy - Ibiblio
www.ibiblio.org/hyperwar/UN/India/RIN/
'The Royal Indian Navy, 1939-1945', [Official History of the Indian Armed Forces in the Second World War]Indian Navy - FIBIwiki
wiki.fibis.org/index.php/Indian_Navy
In 1830 the Bombay Marine was renamed the Indian Navy, based at Bombay. TheIndian Navy, a combatant force, co-operated with the Royal Navy in policingmainbombay - British Maritime History
www.barnettmaritime.co.uk/mainbombay.htm
See below for the Bombay Marine (1686-1830) Indian Navy, Bombay Marine (Ajit Vadakayil: THE INDIAN NAVY MUTINY OF 1946, THE ...
ajitvadakayil.blogspot.com/.../the-indian-navy-mutiny-of-1946-only-war...
Feb 15, 2013 - In 1949, the Indian Navy ( Royal Navy ) revolted. The realization dawned on the crafty English speaking white man, that without the Indian Navy ...
Royal Indian Navy
Kharghar, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra - From your Internet address - Use precise location



No comments:
Post a Comment